The future of mobile networks is rapidly approaching, and with it comes a new generation of technology: 6G. While 5G is still being rolled out and adopted globally, the development and research into 6G are already well underway. This article will explore the key differences between 6G and 5G, examining the potential advancements in speed, latency, capacity, and applications. We will delve into what 6G promises to deliver, comparing it to the current capabilities of 5G networks and highlighting the potential impact on industries, technologies, and our daily lives. Understanding the evolution from 5G to 6G is crucial for anyone interested in the future of communication, connectivity, and the digital landscape.
From significantly faster speeds and ultra-low latency to groundbreaking applications like holographic communication and the tactile internet, 6G is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the world. While 5G represents a significant step forward in mobile network technology, 6G is expected to be a true paradigm shift. Join us as we analyze the projected benefits and challenges of 6G compared to 5G, exploring the potential this next-generation network holds for shaping the future of mobile connectivity. We will discuss the anticipated timeline for 6G deployment, the technological hurdles that need to be overcome, and the exciting possibilities that lie ahead in the era of 6G.
What Is 6G Technology?
6G is the sixth generation of wireless technology, succeeding 5G. It is still largely theoretical and under development, but it promises to be a significant leap forward in mobile communications. Speed is a key factor, with 6G projected to offer data rates up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps). This extreme speed would facilitate advancements in areas like virtual and augmented reality, holographic communication, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Beyond speed, 6G aims to enhance reliability, security, and latency. Ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery. Improved security measures are essential to protect sensitive data transmitted over the network.
6G research also explores innovative technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), terahertz (THz) frequencies, and new antenna designs. These advancements aim to address the growing demands for high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
Differences Between 5G and 6G
While 5G is still being rolled out globally, research and development for 6G is already underway. 6G aims to significantly enhance the capabilities of 5G across several key aspects.
One crucial difference lies in speed. 5G offers peak data rates in the gigabits per second, while 6G is targeting terabits per second. This dramatic increase will enable entirely new applications and experiences.
Latency, or the delay in data transmission, is another area of improvement. 5G brought latency down to milliseconds, and 6G aims to reduce it further to microseconds, or even sub-microseconds. This near-instantaneous communication is crucial for applications like remote surgery and real-time virtual reality.
Coverage is also expected to be significantly enhanced with 6G. While 5G focuses primarily on terrestrial networks, 6G will integrate satellite communication, providing seamless connectivity even in remote or underserved areas.
Finally, 6G will focus on increased reliability and security, building upon the advancements made in 5G to create a more robust and trustworthy network infrastructure.
| Feature | 5G | 6G |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Gigabits per second | Terabits per second |
| Latency | Milliseconds | Microseconds/Sub-microseconds |
| Coverage | Primarily terrestrial | Terrestrial and Satellite Integration |
Speed and Latency Improvements
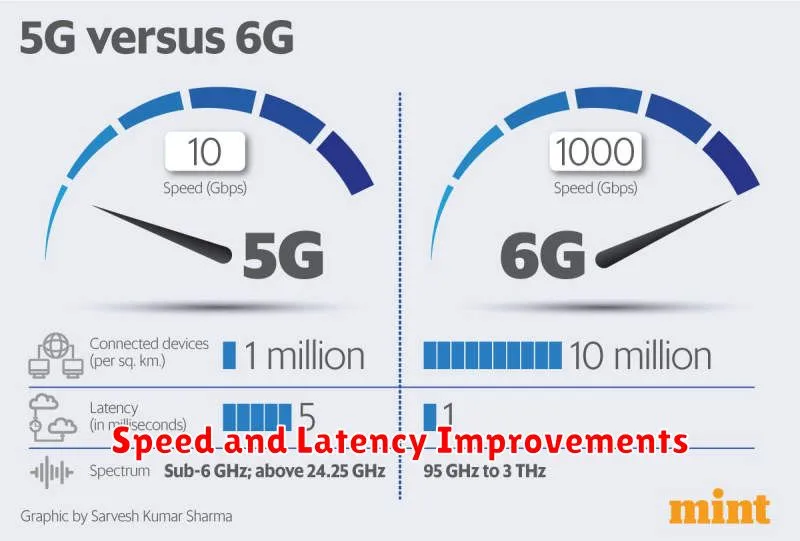
One of the most significant advancements of 6G over 5G lies in its dramatically increased speed and significantly reduced latency. While 5G offers peak speeds of up to 20 Gbps, 6G is projected to reach theoretical speeds of up to 1 Tbps. This represents a 50-fold increase, opening doors to entirely new applications and experiences.
Latency, the delay between sending and receiving data, will also see a substantial improvement. 5G boasts latency as low as 1 millisecond, but 6G aims to reduce this further, targeting latency in the microsecond range. This near-instantaneous communication will be crucial for applications requiring real-time responsiveness, such as remote surgery and autonomous vehicle control.
This table summarizes the key differences:
| Feature | 5G | 6G |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Speed | Up to 20 Gbps | Up to 1 Tbps |
| Latency | Down to 1 ms | Microsecond range |
Use Cases for 6G

While still largely theoretical, 6G is poised to revolutionize various sectors with its unprecedented speed and capabilities. Enhanced Mobile Broadband will offer significantly faster download and upload speeds, supporting seamless Extended Reality (XR) experiences and high-fidelity holographic streaming.
Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) will further enable the Internet of Things (IoT), supporting a massive density of connected devices for applications like smart cities and industrial automation. Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) with near-instantaneous response times will be crucial for time-sensitive applications such as remote surgery and autonomous vehicle control.
Beyond these, 6G is expected to play a pivotal role in enabling advanced applications like digital twins for real-time system monitoring and control, and tactile internet for immersive interactions with remote environments.
Expected Launch Timelines
While 5G is still being rolled out and improved globally, research and development for 6G are already underway. Standardization efforts are expected to solidify around 2028, a crucial step before commercial deployments can begin.
Initial 6G deployments, offering limited coverage and capabilities, are projected for the early 2030s. Widespread availability and adoption, akin to what we see with 4G and 5G today, is likely still further in the future, potentially closer to the latter half of the 2030s.
It’s important to remember that these timelines are estimates, and the actual rollout of 6G may vary based on technological advancements, spectrum allocation, and market demand.
Challenges in Global Deployment
Rolling out 6G globally faces significant hurdles. Spectrum allocation will be a major battlefield, with nations vying for prime bandwidth. Harmonizing these allocations globally will be crucial for seamless interoperability.
Infrastructure development presents another enormous task. The denser network of smaller cells required by 6G necessitates substantial investment and innovative deployment strategies. Reaching remote and underserved areas will pose a particular challenge.
Cost is a critical factor impacting adoption. Both the network infrastructure and user devices will likely be expensive initially, potentially creating a digital divide. Overcoming this requires careful planning and potentially government subsidies.
Security and privacy concerns are also amplified with 6G’s enhanced capabilities. Ensuring robust security protocols and addressing data privacy issues are paramount for building user trust.
What It Means for Users
6G’s advancements translate to a significantly enhanced user experience. Data speeds will be dramatically faster than 5G, allowing for near-instantaneous downloads and seamless streaming of high-resolution content. This opens doors for innovative applications in areas like extended reality (XR) and holographic communication.
Beyond speed, 6G aims for ultra-low latency. This virtually eliminates lag, crucial for real-time applications like remote surgery and autonomous vehicle control. The improved network reliability ensures a consistent connection, even in densely populated areas or challenging environments.
The increased capacity of 6G networks means more devices can connect simultaneously without performance degradation. This is essential for the growing Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, where numerous smart devices require constant network access.